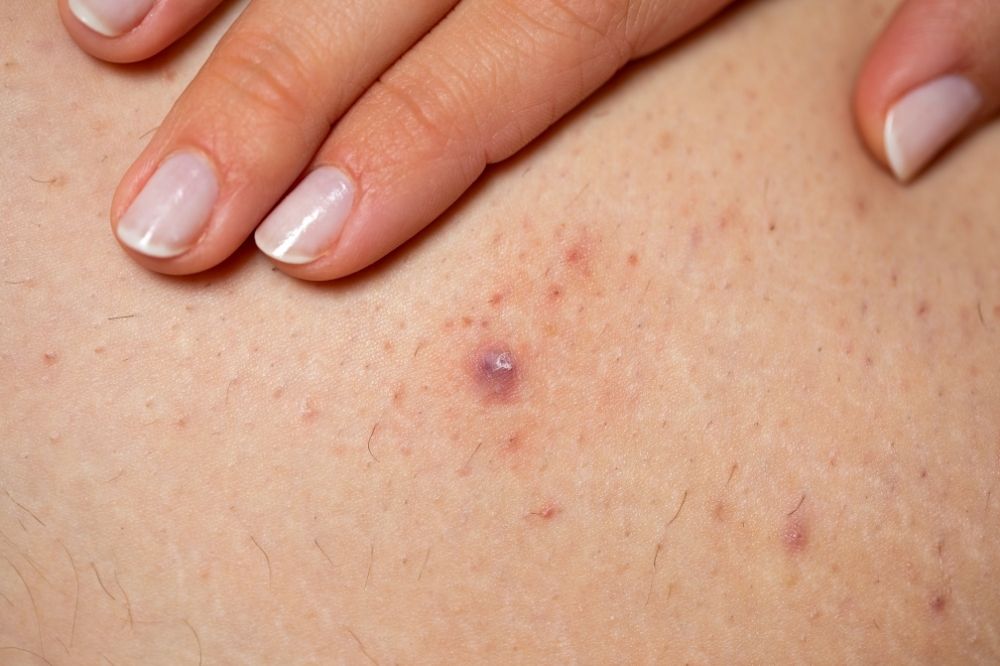
Folliculitis is inflammation of the hair follicle. It can occur on any part of the body that contains hair. It appears as a painful and pus-filled swelling surrounding the hair. It often resolves spontaneously or with simple treatment. It is a common skin disease. It develops due to the inflammation caused by the proliferation of microorganisms in that area after the hair follicle is damaged with any friction and/or pressure. It is most commonly seen in the neck, groin, beard area and genital area. Often the causative agent is bacteria, however fungi and viruses can also cause folliculitis.
What Are the Symptoms of Folliculitis?
It appears as a painful, purulent and red swelling surrounding the hair. It may be accompanied by itching and tenderness. In the following days, crusting can be observed with the oozing of the purulent swelling. Folliculitis, which progresses deeply from the hair root, is called a furuncle. As the inflammation deepens, swelling and tenderness increase.
What are the Causes of Folliculitis?
The most common microorganism causing folliculitis is a bacteria called staphylococcus. Apart from this, viruses, fungi and parasites can also cause folliculitis. The condition of the hair growing back and extending inside the skin before it can reach the surface of the skin is called ingrown hair, and inflammation can develop in this case without any microorganism.
What are the Conditions that Facilitate the Development of Folliculitis?
Factors that facilitate the formation of folliculitis are as follows;
- Hot weather and sweating,
- Obesity,
- Tight skin covering
- Shaving (especially close and irritating shaving)
- Tight clothes that cause friction and prevent sweat from evaporating,
- Presence of certain diseases that reduce the body’s resistance to infectious diseases (such as diabetes, leukemia, AIDS)
- Presence of a skin disease such as puberty acne and/or eczema,
- Injuries that disrupt skin integrity (abrasions, surgical site incisions, other incisions)
- Long-term use of certain medications (corticosteroids and antibiotics)
- a bath in an unclean hot tub.
How Is Folliculitis Diagnosed?
Usually, skin examination is sufficient to make the diagnosis. Sometimes, an examination called bacterial culture and antibiogram may be required to detect the microorganism and to understand which drugs will be effective. For this purpose, a sample is taken from the contents of the pus-filled vesicle and examined in the laboratory.
How Is Folliculitis Treated?
- Conditions that facilitate the formation of folliculitis should be eliminated. (such as losing weight, avoiding environments that cause excessive sweating, wearing loose clothing that allows sweat to pass through, not shaving or using an electric razor)
- The skin area with folliculitis should be kept clean with cleansers to be applied gently.
- Folliculitis should not be squeezed by the patient and the contents should not be emptied. This is very risky and can lead to the spread of the microbe throughout the body and the formation of significant scarring.
- In mild cases, there will be recovery in a few days with warm compresses to be applied to that area.
- In the treatment of more severe, numerous or advanced folliculitis, antibiotics prescribed by your doctor should be applied topically and/or used orally for the duration and as recommended.
- In advanced cases such as furuncles and carbuncles, a minor surgical procedure may be required in the form of an incision on the folliculitis to drain the accumulated pus.