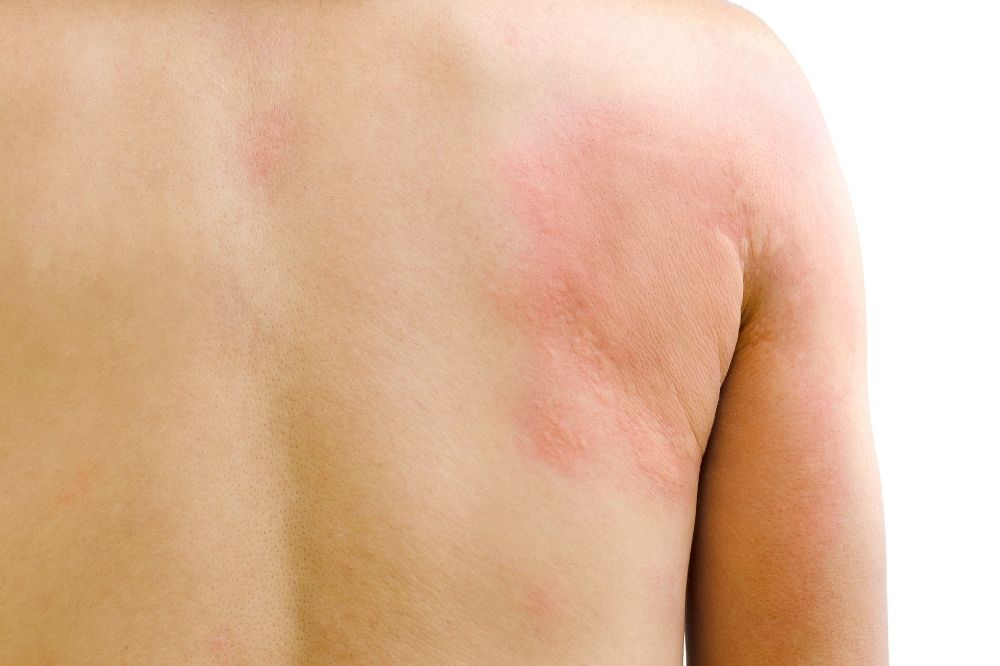
What is Hives (Urticaria)?
Urticaria is a common skin disease characterized by itching attacks that appear as pinkish-red bumps on the skin and disappear in a short time.
What is Angioedema?
Angioedema is a form of urticaria that occurs in the deeper layers of the skin and presents as swelling, burning and stinging sensations. It is often seen in the form of swelling of the eyelids and lips. When the hands and feet are affected, they can be swollen and painful. It can also be seen in the mouth, and in this case, it can lead to serious findings such as shortness of breath and difficulty in swallowing. Angioedema and urticaria can occur separately or together.
What are the Causes of Urticaria and Angioedema?
The cause of the complaints in both is the secretion of histamine by the allergy cells called mast cells in the skin. Physical factors such as exercise, pressure on the skin, heat and cold, foods (such as fish, nuts, tomatoes, strawberries), drugs (muscle relaxants, painkillers, antibiotics) and infections (such as cold and flu) are the factors that can stimulate these cells and cause disease. In some patients with chronic urticaria, the antibodies of the person’s own immune system in the bloodstream stimulate the release of histamine from the mast cells in the skin.
What are the Symptoms of Urticaria and Angioedema?
In urticaria, pinkish-red, itchy, blisters are seen that disappear within 24 hours. These bumps can combine to reach large sizes, or they can stay in small sizes. Angioedema commonly presents as swelling of the eyelids, lips, palms and soles. Sometimes swelling may occur in the mouth and esophagus. In this case, it causes complaints such as shortness of breath and difficulty in swallowing. The regression of angioedema swellings usually takes longer than 24 hours.
How is Urticaria and Angioedema Diagnosed?
Examination findings in urticaria are diagnostic. Some tests can be done to find out the cause. Allergy tests are not required to investigate the causative agent during active disease.
What is Done in the Treatment of Urticaria and Angioedema?
The drugs used are:
- Antihistamine drugs; It is the drugs that are primarily preferred in treatment, which relieves itching and swelling in many patients. Regular use of these drugs on a daily basis is very important for a successful treatment, as they act by preventing the unpleasant symptoms of the disease. In cases where it is not sufficient to suppress the disease, your doctor may increase the dose of your medicine. Some antihistamines can cause distraction and drowsiness, while others have lesser side-effects. Therefore, if you work in jobs that require attention, drive a car and work in jobs that require mental activity, inform your doctor. Since the duration of the disease can vary from person to person, long-term use of medication may be required in some cases.
- In resistant and special cases, drugs that affect the immune system (such as steroids and cyclosporine) or drugs administered by injection (omalizumab) can be used.
- Tongue and throat swelling, although not very common, are angioedema findings. In case of this rare and life-threatening finding, you should consult to the nearest healthcare facility.
What Can I Do to Prevent Urticaria and Angioedema?
The most important thing is to avoid factors that increase urticaria. These can be listed as follows;
- Do not use drugs such as painkillers, antibiotics and muscle relaxants unless absolutely necessary.
- Do not consume alcohol.
- Avoid heavy exercise, extreme heat and cold environments.
- Do not consume foods containing dyes and additives.